Detailed content
Introduction to Optics and Reflection
1.1. What is Optics?
Optics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior and properties of light. It encompasses the study of light's interactions with matter, including reflection, refraction, dispersion, and diffraction.
1.2. Importance of Reflection
Reflection is essential in optics as it allows for the creation of images, the design of optical systems, and the understanding of natural phenomena like the color of objects, the formation of rainbows, and the behavior of light in mirrors.
Understanding Light
2.1. Nature of Light
Light is an electromagnetic wave consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields. It travels in straight lines unless it encounters an obstacle or a change in medium.
2.2. The Speed of Light
In a vacuum, light travels at a constant speed of approximately 299,792 kilometers per second (or about 186,282 miles per second). This speed decreases when light passes through a medium such as air, water, or glass.
Laws of Reflection
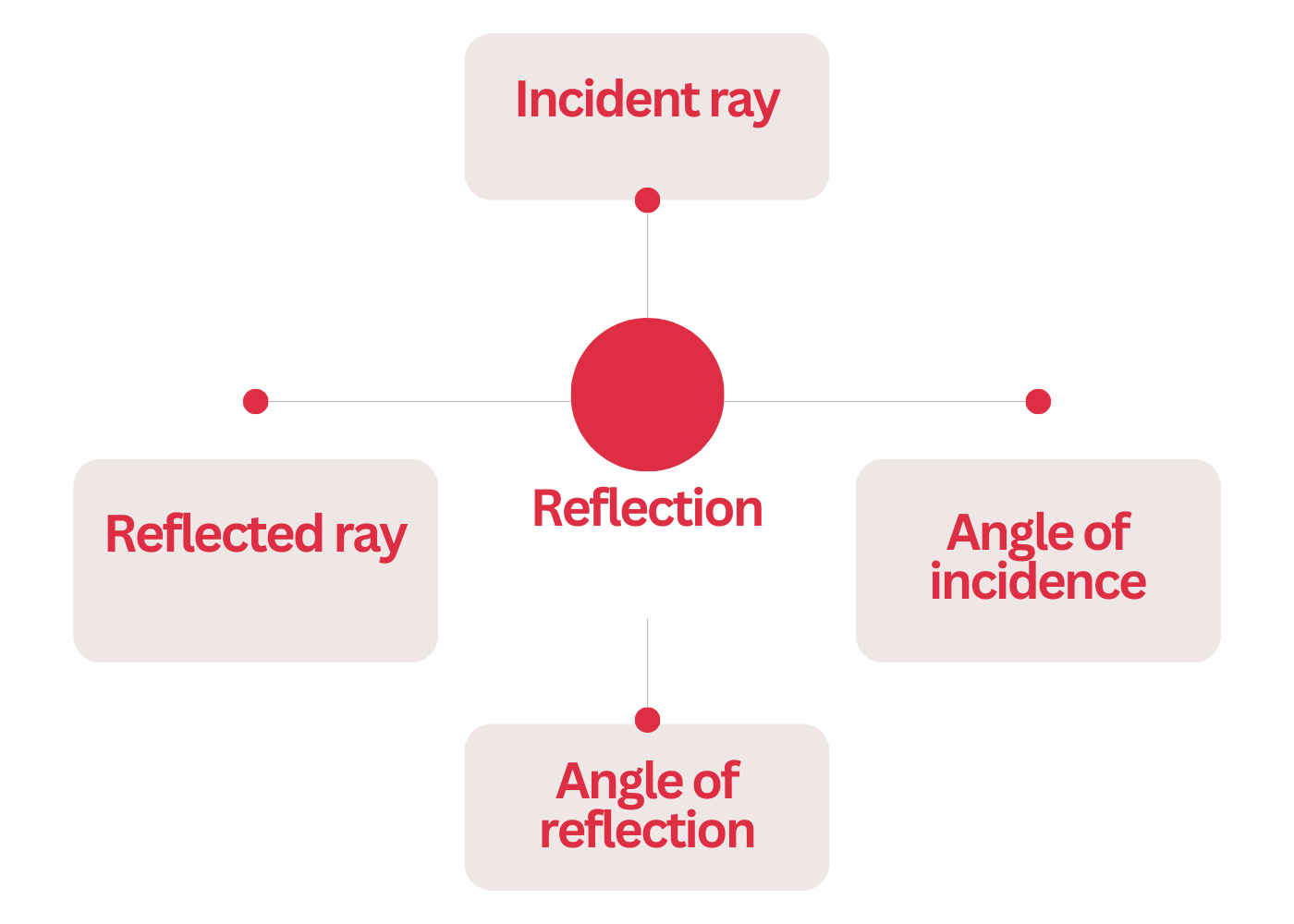
3.1. Incident Ray, Reflected Ray, and Normal
When light strikes a surface, the incoming light ray is called the incident ray. The ray that bounces off the surface is called the reflected ray. The line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence is known as the normal.
3.2. Angle of Incidence and Angle of Reflection
The angle between the incident ray and the normal is known as the angle of incidence (denoted as θi). Similarly, the angle between the reflected ray and the normal is called the angle of reflection (denoted as θr).
3.3. The Law of Reflection
The Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Mathematically, it can be expressed as θi = θr.
Types of Reflection
4.1. Regular Reflection
Regular reflection occurs when light reflects off a smooth surface, such as a mirror. The reflected rays are parallel to each other, resulting in a clear and sharp image.
4.2. Diffuse Reflection
Diffuse reflection occurs when light reflects off a rough or irregular surface, such as paper or matte paint. The reflected rays scatter in different directions, making the surface appear dull.
4.3. Specular Reflection
Specular reflection refers to the reflection of light off a smooth surface in a specific direction. It is responsible for the formation of clear images in mirrors and other polished surfaces.
4.4. Retroreflection
Retroreflection occurs when light is reflected back towards the source, regardless of the angle of incidence. This phenomenon is commonly observed in road signs and reflective clothing.
Applications of Reflection
5.1. Mirrors
Mirrors utilize the principle of reflection to create images. Flat mirrors produce virtual images, while curved mirrors, such as concave and convex mirrors, can produce real or virtual images with various properties.
5.2. Lenses
Lenses, whether convex or concave, rely on reflection and refraction to bend and focus light. They are essential components of optical instruments such as cameras, microscopes, and telescopes.
5.3. Fiber Optics
Fiber optics utilize total internal reflection to transmit light signals over long distances with minimal loss. They are widely used in telecommunications, medical imaging, and data transmission.
5.4. Photography
In photography, reflection plays a crucial role in capturing and manipulating light to create images. Photographers often use reflectors to redirect light and enhance the quality of their photographs.
Advanced Topics in Reflection
6.1. Polarization
Polarization refers to the orientation of light waves in a particular direction. Polarized reflection occurs when light reflects off a surface in a specific polarization state, affecting its properties and applications.
6.2. Multiple Reflections
Multiple reflections occur when light undergoes repeated reflections between two or more surfaces. This phenomenon is exploited in optical cavities, interferometers, and other advanced optical systems.
6.3. Fresnel Equations
Fresnel equations describe the behavior of light when it encounters a boundary between two media with different refractive indices. They are used to calculate reflection and transmission coefficients, crucial for designing optical coatings and anti-reflection coatings.
Conclusion
Reflection is a fundamental phenomenon in optics that governs the behavior of light when it interacts with surfaces. Understanding the laws and principles of reflection is essential for various applications, ranging from everyday objects like mirrors to advanced technologies like fiber optics and laser systems. By studying reflection, scientists and engineers continue to unlock new possibilities for harnessing light in innovative ways, shaping the future of optics and photonics.